The original paper “Recovery management in quicksilver” introduces a transaction manager that’s responsible for managing servers and coordinates transactions. The below notes discusses how this operating system handles failures and how it makes recovery management a first class citizen.
Cleaning up state orphan processes
Key Words: Ophaned, breadcrumbs, stateless
In client/server systems, state gets created that may be orphaned, due to a process crash or some unexpected failure. Regardless, state (e.g. persistent data structures, network resources) need to be cleaned up
Introduction
Key Words: first class citizen, afterthought, quicksilver
Quicksilver asks if we can make recovery a first class citizen since its so critical to the system
Quiz Introduction
Key Words: robust, performance
Users want their cake and eat it too: they want both performance and robustness from failures. But is that possible?
Quicksilver
Key Words: orphaned, memory leaks
IBM identified problems and researched this topic in the early 1980s
Distributed System Structure
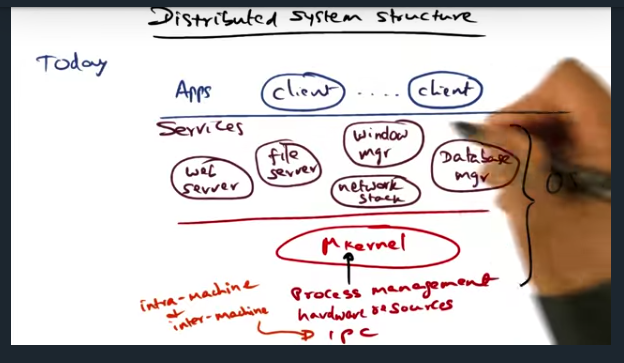
Key Words: microkernel, performance, IPC, RPC
A structure of multiple tiers allows extensibility while maintaining high performance
Quicksilver System Architecture
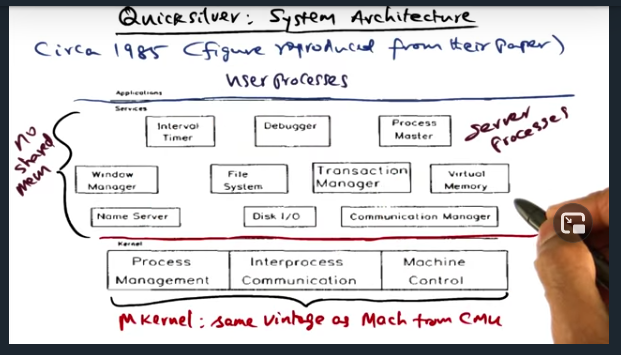
Key Words: transaction manager
Quicksilver is the first network operating system to propose transactions for recovery management. To that end, there’s a “Transaction Manager” available as a system service (implemented as a server process)
IPC Fundamental to System Services
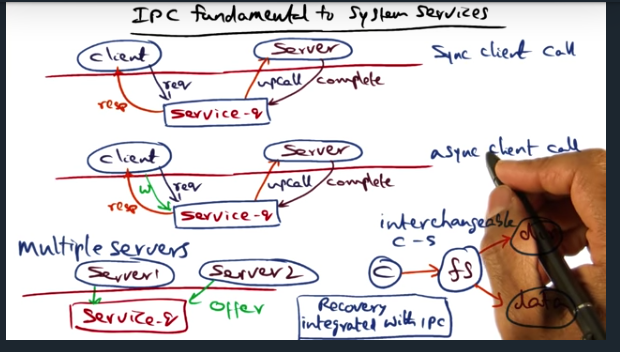
Key Words: upcall, unix socket, service_q data structure, rpc, asynchronous, synchronous, semantics
IPC is fundamental to building system services. And there are two ways to communicate with the service: synchronously (via an upcall) and asynchronously. Either, the center of this IPC communication is the service_q, which allows multiple servers to perform the body of work and allows multiple clients to enqueue their request
Building Distributed IPC and X Actions
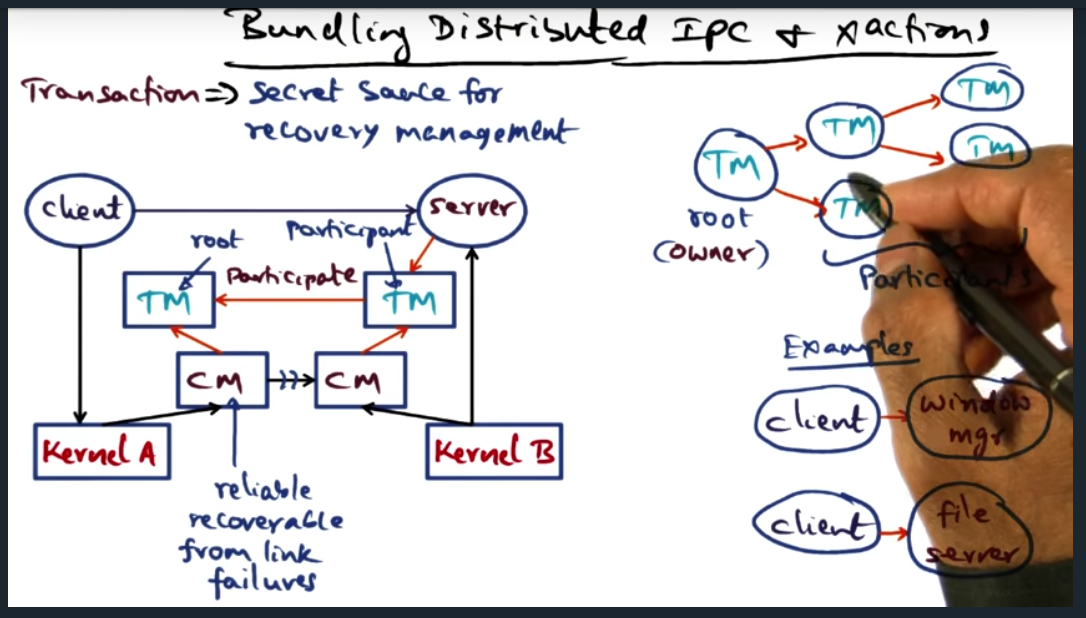
Key Words: transaction, state, transaction link, transaction tree, IPC, atomicity, multi-site atomicity
During a transaction, there is state that should be recoverable in the event of a failure. To this end, we build transactions (provided by the OS), the secret sauce for recovery management
Transaction Management
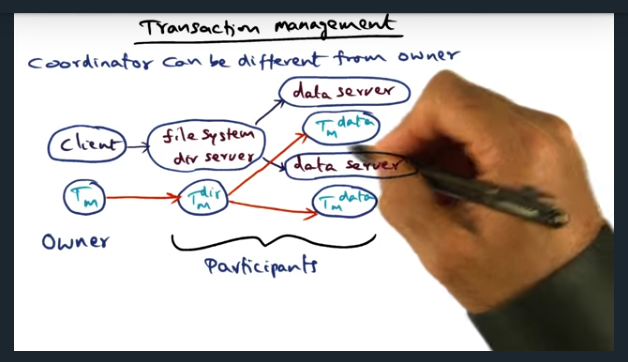
Key Words: transaction, shadow graph structure, tree, failure, transaction manager
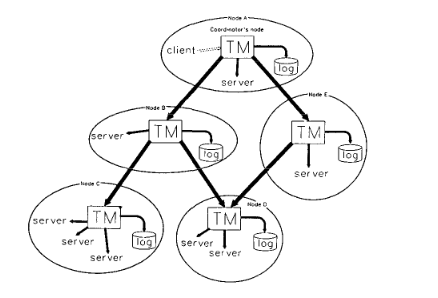
When a client requests a file, the client’s transaction manager becomes the owner (and root) of the transaction tree. Each of the other nodes are participants. However, since client is suspeptible to failing, ownership can be transferred to other participants, allowing the other participants to clean up the state in the event of a failure
Distributed Transaction
Key Words: IPC, failure, checkpoint records, checkpoint, termination
Many types of failures are possible: connection failure, client failure, subordinate transaction manager failure. To handle these failures, transaction managers must periodically store the state of the node into a checkpoint record, which can be used for potential recovery
Commit Initiated by Coordinator
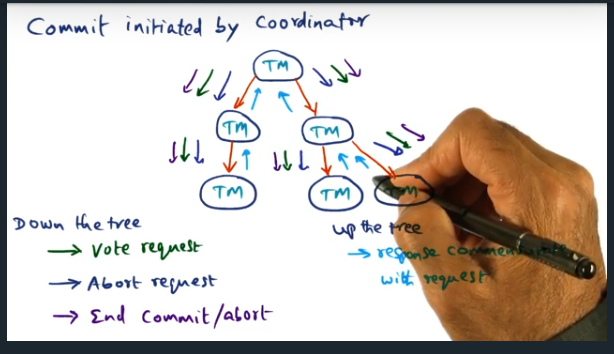
Key Words: Coordinator, two phase commit protocol
Coordinator can send different types of messages down the tree (i.e. vote request, abort request, end commit/abort). These messages help clean up the state of the distributed system. For more complicated systems, like a file system, may need to implement a two phased commit protocol
Upshot of Bundling IPC and Recovery

Key Words: IPC, in memory logs, window of vulnerability, trade offs
No extra communication needed for recovery: just ride on top of IPC. In other words, we have the breadcrumbs and the transaction manager data, which can be recovered
Implementation Notes
Key Words: transaction manager, log force, persistent state, synchronous IO
Need to careful about choosing mechanism available in OS since log force impacts performance heavily, since that requires synchronous IO
Conclusion
Key Words: Storage class memories
Ideas in quicksilver are still present in contemporary systems today. The concepts made their way into LRVM (lightweight recoverable virtual machine) and in 2000, found resurgence in Texas operating system